Lifelong Learning on Permanent Magnet Value Chain
Hereby we offer training for professionals within the thematic orientation Rare Earth Magnets (REM) and Motors, aiming to increase the skills and preparedness for jobs in enterprises that are active along the REM value chain.
The format of the course is blended learning, and it includes both theoretical and practical training to make the learner familiar with the details of the life cycle of Rare Earth Magnets.
The training starts with a digital course “Introduction to Magnetism: Challenges of Rare Earth magnets”. The course is placed on the FutureLearn platform https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/introduction-to-magnetism-the-challenges-of-rare-earth-magnets (module 0) and available for individuals for a fee by the FutureLearn platform. The Basic Concepts of Magnetism course duration is 6 weeks, the study time is 2-4 hours per week. This course is not mandatory but is highly recommended to learners who want to increase their knowledge in magnetism and magnetic materials.
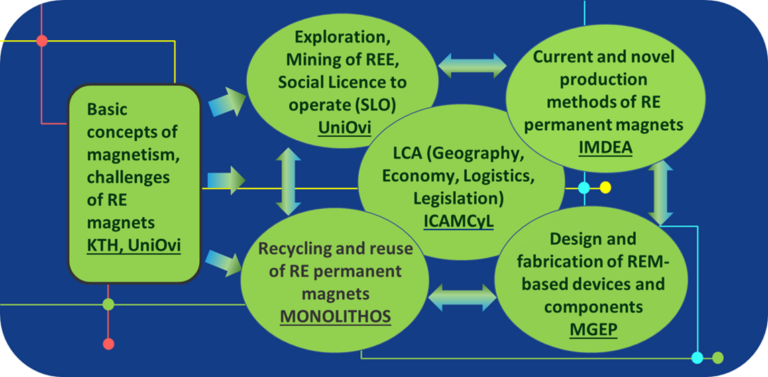
The main part of the course consists of 5 thematic modules, each representing a critical link in the REM value chain.
The duration of the training of each module is one working day (6-8 hours), our students can choose their own course design, either follow the whole course or picking up one or several modules according to their needs.
Structure of the Modules
Module 0: Challenges of Rare Earth Magnets
Module 0 is an introductory course that gives basic knowledge on fundamental concepts of magnetism. The module content is fully digitized and placed on the FutureLearn platform. https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/introduction-to-magnetism-the-challenges-of-rare-earth-magnets
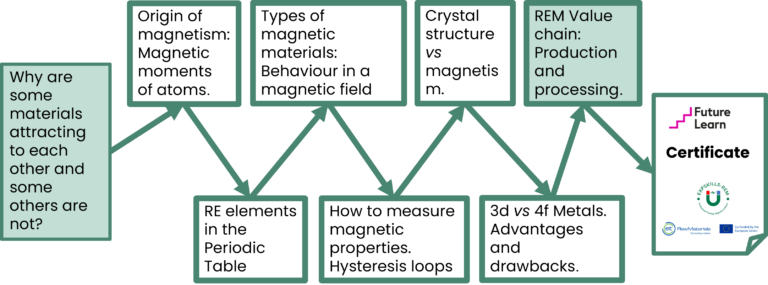
It includes the following topics:



Module 1: Rare Earth Element Ores In Mining
Lesson 1 Rare Earth Element Exploration (REE): The main aspects of REE ores exploration are introduced, along with cases of study from both inside and outside the EU.
Lesson 2 Rare Earth Element Mining (Part I): A review of mining and metallurgical aspects of REE ores is presented, with a special focus on best available technologies (BAT).
Lesson 3 Rare Earth Element Mining (Part II)
Lesson 4 Safety and Environmental Aspects of REE Mining: Quick review of Society & Environment issues in REE ores mining and metallurgy, dealing specifically with the content presented above.
Lesson 5 Social Licence to Operate (SLO) in mining of Rare Earth elements: A practical activity focused on the SLO issues found in REE mining projects at the EU, including a self-critical-analysis exercise.
Lesson 6 Socio-technical toolbox: A practical and ludic activity designed to suggest responsible actions with the aim to change how mining projects are approached, including socio-technical aspects.

Module 2: Current And Novel Production Methods Of Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets (REPM)

Lesson 1 Fully dense REPM production techniques (Part I): The main aspects of the production chain and characteristics of fully dense magnets obtained through sintering routes. These types of magnets can achieve the highest maximum energy product and they are used in high-performance applications such as EVs motors and wind turbine generators, among others.
Lesson 2 Fully dense REPM production techniques (Part II)
Lesson 3 Bonded REPM production techniques (Part I): Here, we will show the production line and characteristics of bonded magnets. These types of magnets possess a lower energy product than fully dense magnets. On the other hand, they show other advantages such as good mechanical properties and higher electrical resistivity.
Lesson 4 Bonded REPM production techniques (Part II)
Lesson 5 Permanent magnet coating: Corrosion protection of REM
Lesson 6 Advanced REPM fabrication techniques (Part I): This activity will cover novel fabrication techniques, mainly focused on metal injection molding (MIM) and additive manufacturing technologies. These fabrication technologies allow for the production of magnets with complex shapes and minimal waste of material.
Lesson 7 Advanced REPM fabrication techniques (Part II)

Module 3: Design And Fabrication Of REM-based Devices And Components

Lesson 1 Introduction to electric motors: Main aspects of EVs motors and wind turbine generators.
Lesson 2 Main design equations for permanent magnet electric motors: Open circuit: Basic equations that help to understand how main design parameters affect the performance of the motor.
Lesson 3 Magnetic materials in the electric motor applications
Lesson 4 Permanent magnet performance calculation: Here we demonstrate how to calculate parameters characterizing performance of permanent magnets.
Lesson 5 Demagnetization problems in electric motors
Lesson 6 Practical issues on size calculation: Demonstration of practical issues for calculating and optimizing machine dimensions


Module 4: Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Recycling

Lesson 1 Introduction to Rare Earth permanent magnets (Part I)
Lesson 2 Introduction to Rare Earth permanent magnets (Part II)
Lesson 3 Recycling of REE’s from permanent magnets (Part I)
Lesson 4 Recycling of REEs from permanent magnets (Part II)
Lesson 5 Pre-processing methods for REEs recovery from permanent magnets
Lesson 6 Hydrometallurgical recovery of REEs from permanent magnets based on MONOLITHOS’ recycling method

Module 5: Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)

Lesson 1 Introduction to LCA: The key aspects related to LCA will be introduced, together with research cases from both inside and outside the EU.
Lesson 2 Types and Benefits of LCA: A review of the types and benefits of LCA will be presented, with a special focus on the benefits of LCA.
Lesson 3 Sustainable Recycling of Permanent Magnets: In this activity, the types/key properties/applications of permanent magnets will be shortly overviewed. The importance of recycling will be emphasized in connection to modern recycling methods.
Lesson 4 Life Cycle Assessment of Magnets and Environmental Impacts: The Life Cycle Assessment of Magnets and Environmental impacts will be presented in this activity.



